Description
Product details
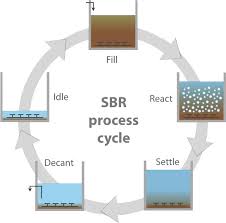
The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a fill-and- draw activated sludge system for wastewater treatment. In this system, wastewater is added to a single “batch” reactor, treated to remove undesirable components. A Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) is a type of activated sludge wastewater treatment system that utilizes a fill-and-draw process where all stages of treatment occur sequentially in a single tank. Unlike conventional continuous flow systems that require separate tanks for each process (e.g., equalization, aeration, clarification), SBRs integrate these stages into a single reactor operated in a timed sequence. How SBR wastewater treatment works The SBR treatment cycle typically consists of five sequential phases: Fill: Wastewater is pumped into the SBR tank, where it mixes with the activated sludge (biomass) from the previous cycle. React: Air is supplied to the tank via an aeration system, providing oxygen for the microorganisms to break down organic pollutants (BOD, ammonia, nitrogen). Settle: Aeration stops, allowing the activated sludge to settle at the bottom of the tank due to gravity, leaving clear, treated water above. Decant: The clear, treated water (supernatant) is removed from the tank without disturbing the settled sludge. Idle: This is a waiting period before the next fill phase, during which excess sludge can be removed. Advantages of SBR wastewater treatment Compact Footprint: SBRs require less space compared to conventional systems as all treatment stages happen in a single tank, making them suitable for areas with limited land availability. Operational Flexibility: SBRs are adaptable to varying flow rates and organic loads, making them suitable for industrial and municipal applications with fluctuating wastewater characteristics. High Treatment Efficiency: SBRs can achieve high removal efficiencies for organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus due to the controlled aeration and anoxic/anaerobic cycles. Nutrient Removal: SBRs can effectively remove nitrogen and phosphorus without the need for chemical addition, promoting biological nutrient removal (BNR). Reduced Odor: Aerobic conditions throughout much of the cycle minimize odor generation compared to anaerobic systems. Automated Operation: Modern SBR systems are highly automated, reducing the need for constant manual oversight. Potential for Water Reuse: The high-quality effluent produced by SBRs can be suitable for various reuse applications after further disinfection and filtration. Applications of SBR wastewater treatment SBR technology is used in various municipal and industrial wastewater treatment settings, including: Small to medium-sized municipal plants Industrial applications such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing Remote or decentralized facilities Upgrading existing plants Advanced SBR systems like the Hybrid Granular SBR (GST) can improve efficiency using bio-beads that help retain biomass, leading to better removal of organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. GST systems also reduce the need for certain equipment, resulting in a smaller size and lower costs.