Description
Product details
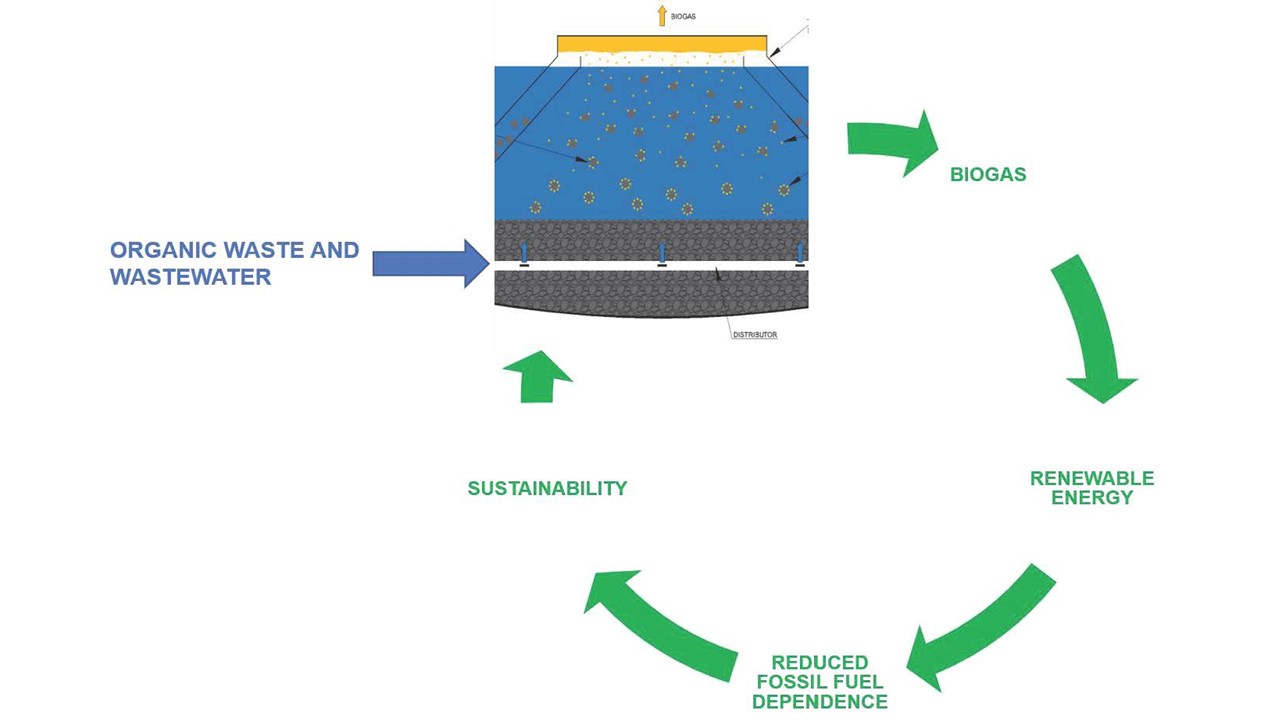
An upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor is a type of anaerobic digester used for wastewater treatment, particularly for high-strength industrial wastewater. It's a single-tank process where wastewater flows upwards through a suspended blanket of granular sludge, breaking down organic pollutants and producing biogas. This technology is known for its efficiency in removing organic matter and its ability to produce usable biogas. How it works Wastewater inflow: Raw wastewater enters the reactor from the bottom. Sludge blanket contact: It flows upward through a dense blanket of granular sludge (microbial aggregates). Anaerobic degradation: Anaerobic microorganisms within the sludge blanket break down organic pollutants in the wastewater through anaerobic digestion. Biogas production: This process generates biogas, primarily methane and carbon dioxide, which bubbles upward, providing mixing and contributing to energy recovery potential. Phase separation: A gas-liquid-solid separator at the top of the reactor separates the treated liquid effluent, biogas, and sludge particles, returning the sludge to the digestion compartment. Effluent discharge/post-treatment: The treated effluent, with significantly reduced organic load (BOD and COD), can then be discharged or undergo further treatment for removal of nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) and pathogens. Advantages High organic loading capacity: Capable of effectively treating wastewater with high organic loads. Energy generation: Produces biogas (methane) as a renewable energy source that can be captured and utilized. Low sludge production: Generates a smaller quantity of stabilized sludge compared to aerobic systems, reducing sludge handling and disposal costs. Low energy requirements: Operates without the need for energy-intensive aeration systems common in aerobic treatments. Low land requirements: Compact design compared to conventional systems. Relatively simple design and operation. Applications UASB reactors are particularly well-suited for treating: Industrial wastewater: Examples include wastewater from industries like breweries, distilleries, food processing, pulp and paper, and tanneries, as well as agricultural wastes. High-strength wastewaters with high carbohydrate content.